SAP ECC VS SAP S/4HANA – Key Changes
SAP S/4HANA can run only on the HANA database. This is completely different from SAP ECC. SAP ECC can run on Oracle, IBM DB2, etc. SAP S/4HANA leverages SAP HANA’s in-memory capabilities and design principles.
The HANA in-memory database reads data faster than traditional databases that fetch data from the hard disk. This is because data is read from memory, i.e., data resides in the main memory RAM (though Write happens in hard disk).
HANA’s column-based tables enable faster access (since only affected columns need to be read in a query), better compression (because only distinct values are compared to rows), parallel processing (different columns can be easily processed parallelly)
OLTP and OLAP capabilities are available in the same system. They offer real-time reporting and predictive analysis.
There will be no aggregate (total), index, and history tables in SAP S4HANA. This is due to dynamic aggregate creations on the fly based on line item tables.
The classic General Ledger contains all the financial transactions of a business. Besides using the classic general Ledger, businesses make use of the Special Ledger and other components like Profit Center Accounting (PCA) to meet statutory as well as internal requirements. SAP Profit Center Accounting and the special Ledger reside in separate applications. Therefore, these modules were not automatically reconciled with the classic General Ledger. Due to this, there was a need to perform additional closing activities to reconcile these additional modules with the classic General Ledger.
New General Ledger: Classic GL is no longer available in S/4, New Universal Journal.
The new General Ledger uses the same familiar interface as the classic general Ledger but overcomes the difficulty encountered while carrying out the closing activities in the classic General Ledger.
The New General Ledger uses the Special Purpose Ledger to save total values in the tables. All company codes are assigned to a leading Ledger. For each client, additional ledgers for each company code can be added. These additional ledgers can be used for different purposes such as parallel accounting or management reporting. With the New General Ledger it is now possible to perform postings that previously required several components. This is also true with regards to the transfer postings between profit centers that were previously stored and the Special Ledger.
The new General Ledger makes use of additional tables and fields as compared to the classic general Ledger once the new Gen functionality is activated, the previous financial accounting menu is replaced by the financial accounting (new) and General Ledger (new) menu. It is required to activate the new general Ledger accounting so that the transactional data is written to the new tables rather than the classic general Ledger tables.
Business partners: Customers, Contacts, and vendors are no more! The traditional transactions such as XD3, VAP3 and XK3 are obsolete and will simply redirect you to the transaction BP.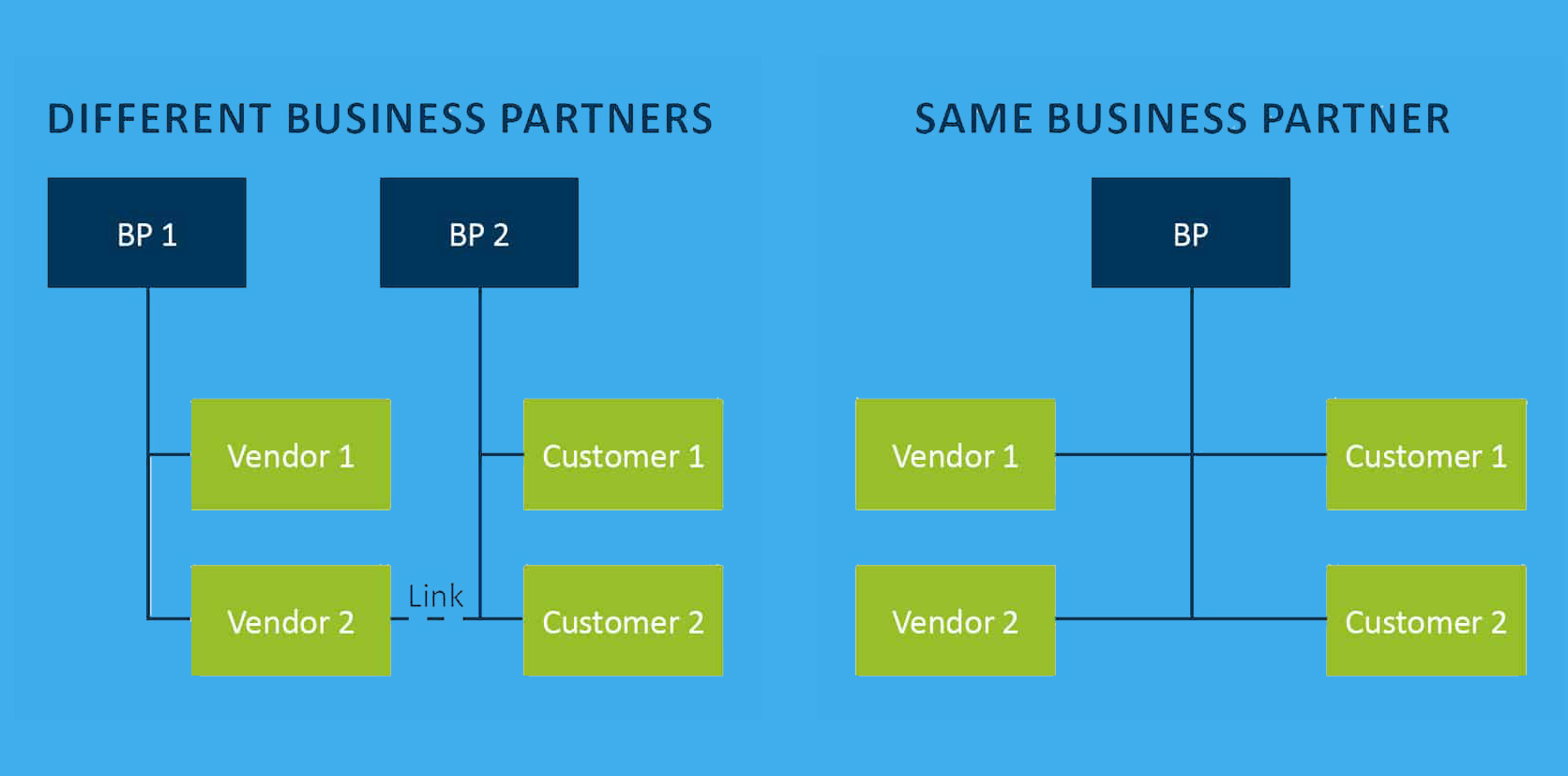
In SAP S/4HANA, Customer and vendor master data need to be integrated/migrated as Business Partner. Customer-vendor integration (CVI) is a mandatory step to run business with SAP S/4HANA.
One key difference between SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA is that the Material number can now be 40 characters instead of the existing 18 in SAP ECC. This is an optional feature. Therefore, the impacts of this extension on interfaces, custom coding, and other SAP applications must be evaluated. This must be done before switching to 40 characters. You can refer to note number 2267140 for more details.
Credit management: Traditional SD credit management has been turbocharged in S/4 with greatly increased functionality.
There is a new credit management system in SAP S/4HANA by the name of FSCM-CR. It is the credit management of Financial supply chain management. It replaces SAP ECC’s FI-AR-CR. FSCM-CR is built on a distributed architecture. This allows interfaces with external credit rating agencies. Traditional SAP ECC’s FI-AR-CR credit control setting requires a high degree of manual work. Also, FSCM-CR has valuable advanced features like
Automatic risk scoring & credit limit calculations with a credit rule engine
Automatic update to master data based on the approval of credit limit
Workflow for credit events
Foreign trade: Foreign trade data has been shipped out to SAP GTS. However, since version S/4 HANA, brought back into scope legal control, embargos and intrastate reporting. Everything else…now in SAP GTS only.
GTS (Global trade services) in SAP S/4HANA replaces the foreign trade functionality in SAP ECC. A few of the features in GTS w.r.t foreign trade are
SPL (Sanctioned party list) screening.
Automated embargo check. A process which requires manual effort in SAP ECC.
Automatic & Simplified license checks in SAP S/4HANA. License checks in SAP ECC were complex and required a lot of manual effort.
Automatic import/export declaration
ATP: Advanced ATP is new to S/4 – features like location substitution – automating STOs between plants based on ATP rules.
the traditional SAP ECC system, conventional Available-to-Promise (ATP) is the order fulfillment process that is designed to provide a commitment to customer-requested order quantities and dates based on availability of products. The availability check ensures that there are enough components available for planned or production orders in production planning and production control. It is an important function in the supply chain and is easy to use and implement, although it does not always offer customers the depth of functionality they were looking for. Further functionality is obtained by implementing SAP Advanced Planning and Optimisation (APO) but entails much more complexity in use and implementation.
The increased complexity of models in today’s digital world, where more complex mechanisms are necessary for varied production, variable demand and multiple stock localisations, led to the fact that SAP conventional ATP has become insufficient. To cope with all these changes and to adhere to the new S/4HANA value levers (agility, efficiency and effectiveness) SAP has developed ATP (advanced Available-to-Promise) which addresses the challenge of working in a dynamic and moving environment allowing organizations to thrive (instead of getting caught like a deer in headlights) as a result of this new dynamic and moving business environment.
Warehouse Management: The SAP solution for WM is now extended warehouse management (EWM), either embedded as a native integration or as a side-car approach. The old WM is still available, but for how long is not clear as SAP have expressed their intention to retire it.
SAP’s new application for warehouse management, EWM replaces the existing WM module. There will be 2 options
Native integration i.e inbuilt in SAP S/4HANA
Sidecar approach for decentralized deployment
New tables: There are many new tables you should be aware of in S/4, especially if you are upgrading from an ECC6.0 system rather than carrying out a greenfield implementation.
Internal tables are used to obtain data from a fixed structure for dynamic use in ABAP. Each line in the internal table has the same field structure. The main use for internal tables is for storing and formatting data from a database table within a program.
Work Area
Work areas are single rows of data. They should have the same format as any of the internal tables. It is used to process the data in an internal table one line at a time.
There are two types of internal tables.
- Internal tables with HEADER line
- Internal tables without HEADER line.
Material Master Material number field extended to 40 characters from 18 characters
Transaction OMSL allows customer-specific settings regarding the material number field length. Here the settings need to be adapted to allow a field length of more than 18 characters
Define Output Format of Material Number can be accessed via — IMG (Logistics General — Material Master — Basic Settings).
It´s recommended to execute conversion pre-check (for details see SAP Note: 22169580). For the conversion of selection, variants see SAP Note 1696821 for details
Restrictions need to pre-check.
SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition 1511 restriction note (general): 2214213
Collection of restriction related to MFLE: 2233100.
- ALE generation for BAPIs: SAP Note 2232497
- Extended Material Number in Suite Integration: SAP Note 2232396
- Extended Material Number Display in Archived Data: SAP Note 2232391
- Length of Customer and Supplier Material Number: SAP Note 2232366
- Extended Material Number in LIS: SAP Note 2232362
- Product Structure Browser: SAP Note 2229892
- Characteristic Values in PLM: SAP Note 2229860
Revenue recognition: Another turbocharge from SAP, with Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) being spawned.
SAP S/4HANA’s Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) replaces SAP ECC SD Revenue Recognition. This is due to new accounting standards released jointly by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The new guideline is also in IFRS 15.
SAP ECC’s SD Revenue Recognition is based on Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (US-GAAP), International Accounting Standards (IAS)/Financial Reporting Standards (FRS). Therefore, it provides the option of recognizing revenue based on an event (like Goods issue, proof of delivery ) or over some time (based on a specific set of dates) apart from the standard way of realizing revenue on billing.
The new standard introduces a 5 step model.
Identify the contract
Separate performance obligations
Determine transaction price
Allocate transaction price
Recognize revenue
Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) in SAP S/4HANA accounts for fundamental changes with IFRS 15. Moreover, it also meets the requirements of parallel accounting and cost recognition.
Output management: By definition output management across all functions will now use the Business Rules Framework (BRF+). The option to stay with your traditional NAST approach is still available, with small configuration settings.
SAP S/4HANA’s Business rule framework plus (BRF +) replaces SAP ECC’s message determination with the NAST table. Also, the target architecture is based on Adobe Document Server and Adobe forms only. Please use OSS note 2228611 for more details.




